ARTICLES
Best Practices for Securing Your Home Network
Don't be a victim! Malicious cyber actors may leverage your home network to gain
access to personal, private, and confidential information. Help protect yourself, your
family, and your work by practicing cybersecurity-aware behaviors, observing some
basic configuration guidelines, and implementing the following mitigations on your home
network, including:
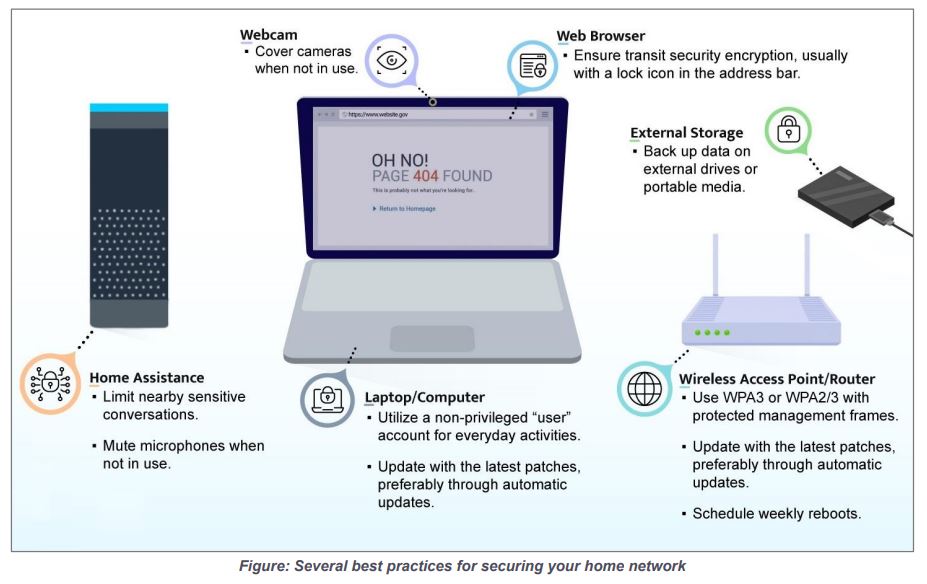
* Upgrade and update all equipment and software regularly, including routing
devices
* Exercise secure habits by backing up your data and disconnecting devices when
connections are not needed
* Limit administration to the internal network only
Recommendations for device security
Electronic computing devices, including computers, laptops, printers, mobile phones,
tablets, security cameras, home appliances, cars, and other “Internet of Things” (IoT)
devices must all be secured to reduce the risk of compromise. Most home
entertainment and utility devices, such as home monitoring systems, baby monitors, IoT
devices, smart devices, Blu-ray™ players, streaming video players, and video game
consoles, are capable of accessing the Internet, recording audio, and/or capturing
video. Implementing security measures can ensure these devices don’t become the
weak link in your home protection.
Upgrade to a modern operating system and keep it up-to-date
The most recent version of any operating system (OS) contains security features not
found in previous versions. Many of these security features are enabled by default and
help prevent common attack vectors. Increase the difficulty for an adversary to gain
privileged access by using the latest available and supported OS for desktops, laptops,
and smart devices. IoT devices on a home network are often overlooked, but also
require updates. Enable automatic update functionality when available. If automatic
updates are not possible, download and install patches and updates from a trusted
vendor on a monthly basis.
Secure routing devices and keep them up-to-date
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) may provide a modem/router as part of your
service contract. To maximize administrative control over the routing and wireless
features of your home network, consider using a personally owned routing device that
connects to the ISP-provided modem/router. In addition, use modern router features to
create a separate wireless network for guests, for network separation from your more
trusted and private devices.
Your router is the gateway into your home network. Without proper security and
patching, it is more likely to be compromised, which can lead to the compromise of
other devices on the network as well. To minimize vulnerabilities and improve security,
the routing devices on your home network should be updated to the latest patches,
preferably through automatic updates. These devices should also be replaced when
they reach end-of-life (EOL) for support. This ensures that all devices can continue to
be updated and patched as vulnerabilities are discovered.